Advertisement
Rise in Hong Kong infant eczema cases linked to pandemic cleaning habits
Academics at Chinese University of Hong Kong also say they have developed new probiotics for children and adults to target skin condition
Reading Time:3 minutes
Why you can trust SCMP
15

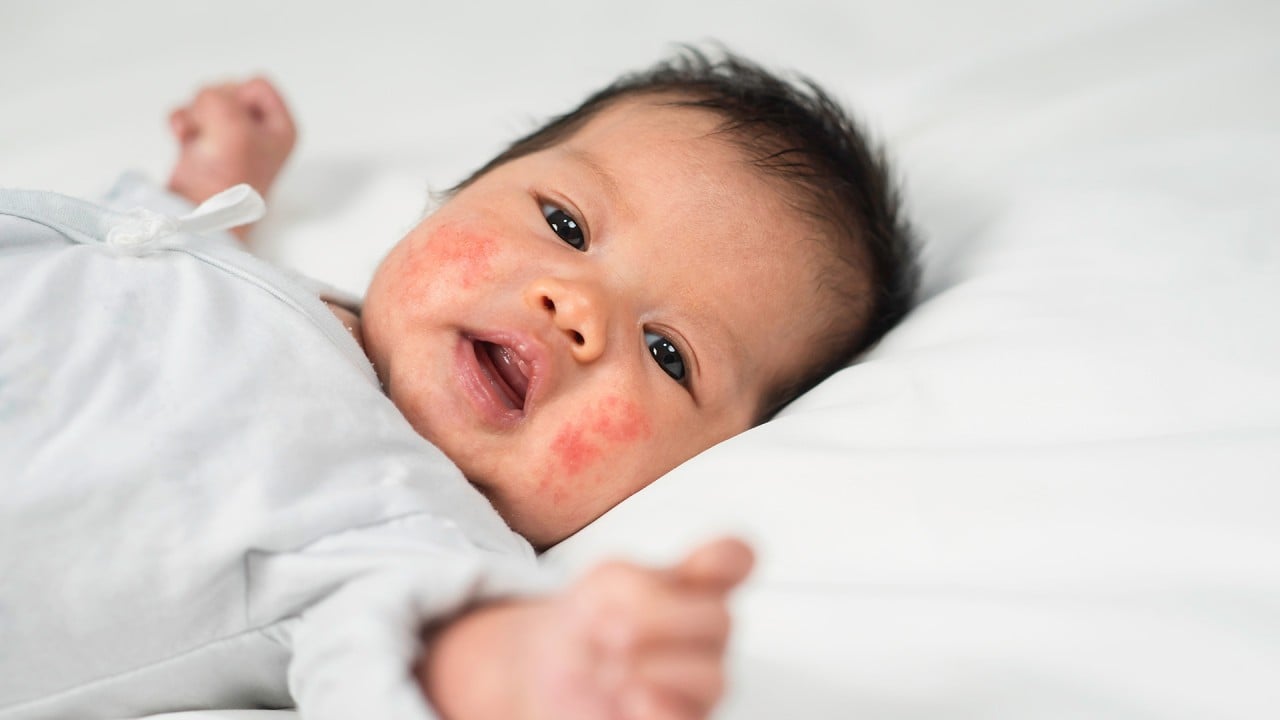
“Excessive” cleaning practices during the Covid-19 pandemic are likely to have caused a 46 per cent increase in cases of conditions such as eczema among infants in Hong Kong due to lowered bacterial immunity, university researchers have said.
Academics at the Chinese University of Hong Kong’s faculty of medicine also said they had developed new probiotics that could reduce the severity of the skin condition among infants in three months.
“The number of new cases of eczema in children has increased substantially after the Covid-19 pandemic, and we believe this is closely linked to changes in hygiene and sanitation habits,” said Leung Ting-fan, a paediatrics professor at the university.
Atopic dermatitis, often referred to as eczema, is a condition that can cause redness, irritation and itchiness of the skin.
According to the American Academy of Paediatrics, atopic diseases are caused by allergic reactions that see the body produce an exaggerated response.
Advertisement